By Benadetta Chiwanda Mia:
The Reserve Bank of Malawi’s latest National Payment Systems (NPS) report shows a 14.3 percent increase in transaction volumes to 527.9 million and a 23.4 percent rise in transaction value to K59.5 trillion in the third quarter of 2024.
The increase is attributed to the end of the agricultural trading season, which boosted economic activities and interbank transactions.
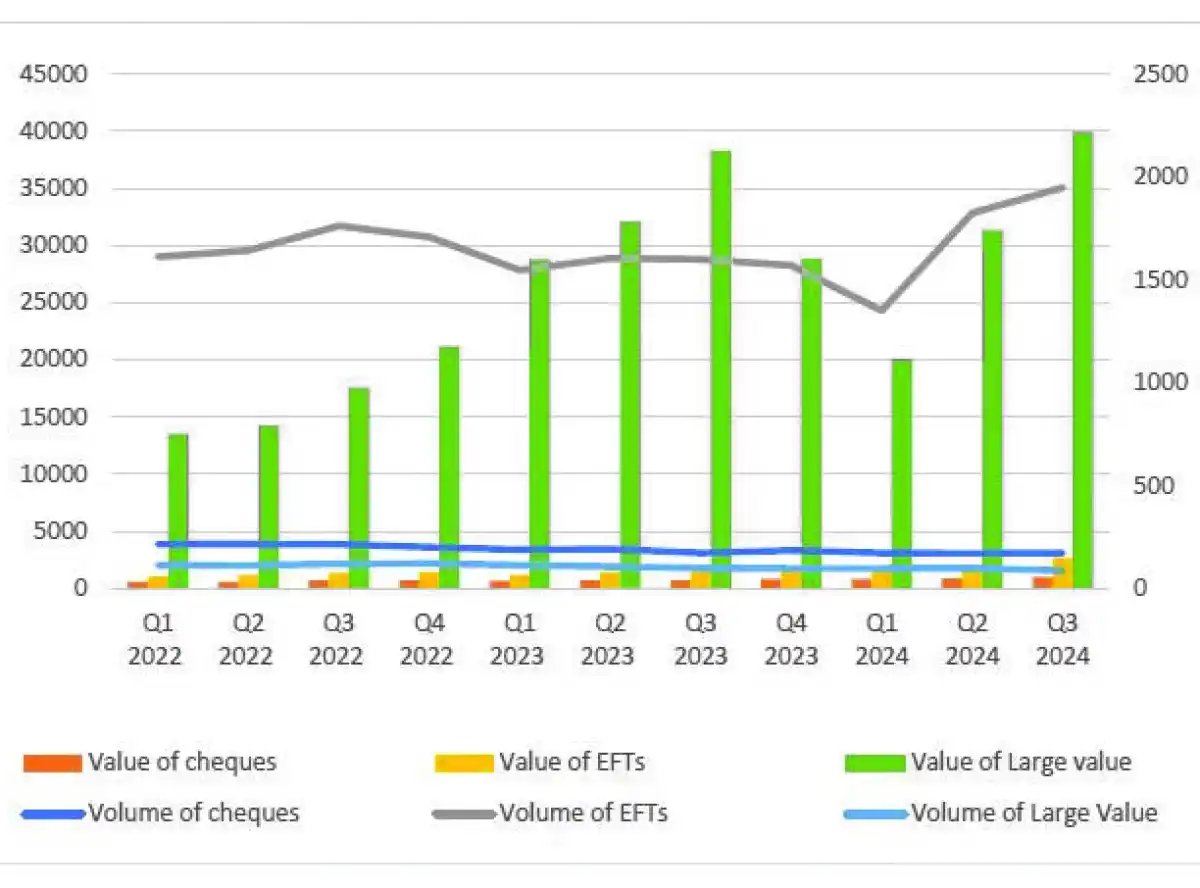
The Malawi Interbank Transfer and Settlement System (MITASS) was a significant contributor, accounting for 73.3 percent of the total transaction value.
The report further shows that MITASS transactions saw a 5.4 percent increase in volume and a remarkable 26.9 percent rise in value, reaching 2.2 million transactions worth K43.6 trillion.
This growth was driven by electronic funds transfer transactions, which rose by 6.8 percent to 2.7 million, and Real Time Gross Settlement transactions, which experienced a substantial 56.3 percent increase.
Cheque transactions also recorded modest growth, with volumes increasing by 1.5 percent to 173,728 and the transaction value climbing by 12 percent to K1 trillion.
Year-on-year comparisons showed a slight 0.1 percent rise in cheque volumes but a significant 37 percent increase in transaction values, indicating continued reliance on cheques for high-value transactions.
“Digital Financial Services saw a notable expansion, with transaction volumes rising by 14.8 percent to 516.3 million and the transaction value increasing by 17.6 percent to K10.4 trillion. Mobile money services also experienced growth, with subscriber numbers increasing by 3.8 percent to 14.8 million and registered mobile money agents rising by 12.6 percent to 447,348.
“Internet banking services also experienced growth, with subscribers increasing by 5.3 percent to 298,750. Transaction volumes and values rose by 7.4 percent and 11.3 percent, respectively, reaching 1.9 million transactions worth K3.7 trillion,” the report reads.
Despite these gains, the central bank pointed out that mobile money use remains limited, with airtime top-ups accounting for 44.5 percent of transactions and cash-in/cash-out processes comprising 33.4 percent.
Furthermore, the RBM report highlighted several ongoing challenges, including low female participation, limited access points in rural areas, low activity rates among mobile money users, high transaction fees, and a rise in fraud cases.
ICT Association of Malawi (Ictam) General Secretary Exile Njoka said the performance demonstrates that the payment ecosystem is evolving and growing in the right direction as evidenced by the increase in volume and value of instant transfers and mobile money transactions.
However, he called for intensified financial education campaigns tailored for women and providing incentives for female entrepreneurs to use digital financial services, to improve their participation in digital financial services.
“Female participation in digital financial services is hindered by socio-cultural barriers, lack of financial literacy, and limited access to mobile phones and digital tools. Despite industry-wide campaigns, women’s access to mobile money platforms has not significantly improved, reflecting a need for targeted interventions,” Njoka said.
Reacting to the developments, Consumers Association of Malawi (Cama) Executive Director, John Kapito has challenged the central bank and the mobile money service providers, including banks to put robust systems that stamp out increasing fraud.
“The fraud cases are increasing and have affected the perception of mobile money instead of growing the service to replace cash transactions. They need to have systems that are more trackable to root out the fraudsters and protect the customers,” Kapito said.
Economic expert Mavin Banda described the growth as a positive indicator on the path to establishing the non-fungible RBM-backed digital Kwacha.
He noted that the positive annual growth trend reflected the industry’s ongoing efforts to expand the payments ecosystem, serving as a catalyst for economic growth, stability, and development.
“What is also not surprising is the dominance of MITASS transactions which is due to transactions such as salary payments, procurement payments and other large business payments. The disincentive to hold cash is also a great thing because what people don’t recognise is that it takes money to print money and with the hastened adoption of electronic settlement, the demand for cash drops, thus the requirement to replace damaged money reduces and offers reprieve for the RBM,” Banda said.








0 Comments