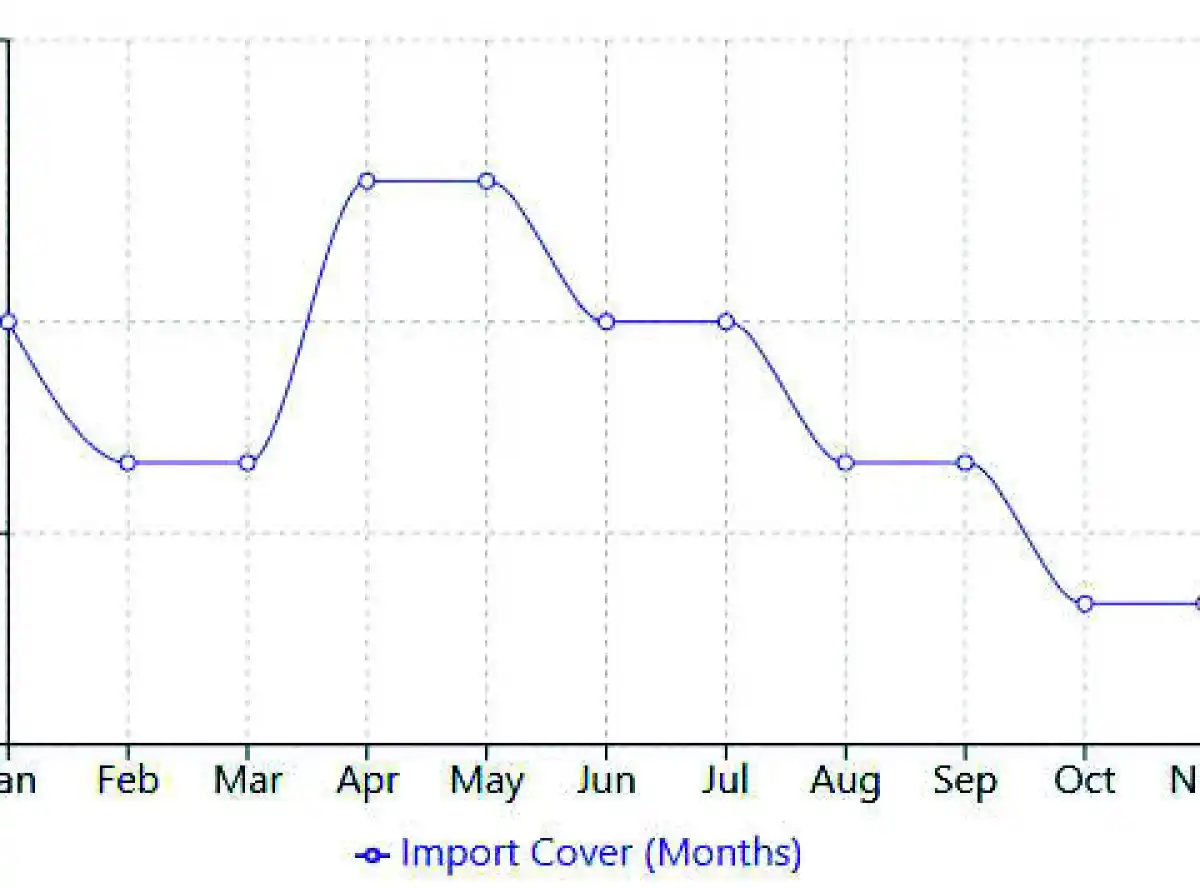
Malawi’s total foreign exchange reserves averaged 2.2 months of import cover in 2024, falling significantly short of the internationally recommended three-month threshold.
This persistent sub-optimal reserve level raises questions about the country’s economic vulnerability and potential challenges in managing international trade and financial stability.
A Malawi Financial Market Update for the week ending February 28 2025, published by Bridgepath Capital Limited, shows that, in January 2024, total reserves stood at $576.70 million (2.3 months of imports).
In February, the forex reserves took a slight dip to $540.32 million (2.2 months of imports), signalling early signs of economic pressure.
The reserves registered a peak in April, reaching $603.07 million (2.4 months of imports), representing the highest level.
By October, reserves had fallen to $519.0 million (2.1 months of imports) before a slight peak to $530.9 million (2.1 months of imports).
A Monthly Economic Review for December 2024, published by the Reserve Bank of Malawi, shows that official reserves were recorded at 0.6 months import in December.
In an interview on Wednesday, economist Exley Silumbu said the foreign exchange challenge had become perpetual.
“If you look across the board, the resources of foreign exchange earnings have not been really satisfactory in order to relieve the country of the foreign exchange constraint,” Silumbu said.

Another economic expert Velli Nyirongo said Malawi’s foreign exchange reserves in 2024 revealed a precarious economic position.
He said the fluctuations highlighted economic volatility, culminating in a concerning low of 0.6 months of import cover by December.
“This persistent deficit indicates a substantial trade imbalance, with imports consistently exceeding exports, placing continuous pressure on the Kwacha.
“Critically, low reserve levels constrain Malawi’s ability to withstand external economic shocks and finance essential imports, potentially leading to supply shortages and inflationary pressures. Furthermore, forex shortage hinders private sector growth and foreign investment, impeding economic development,” Nyirongo said.








0 Comments